In the digital age, where speed and efficiency reign supreme, a Content Delivery Network (CDN)...
How CDN Works: A Comprehensive Breakdown 2024
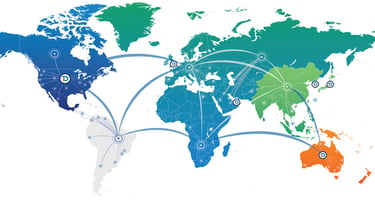
In the fast-paced world of online content delivery, Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a pivotal role in ensuring that digital content is efficiently and securely delivered to users worldwide, irrespective of their location and the device they are using. A CDN is essentially a network of geographically distributed servers that work together to provide fast delivery of internet content by caching content at the network edge, which optimizes website performance and user experience.
Understanding CDN and Its Mechanism
A CDN's primary function is to reduce the physical distance between the server and the user, thus minimizing latency and speeding up the load time of web pages, images, videos, and other content. This is achieved by storing cached versions of content on multiple servers around the world. When a user requests a webpage that is part of a CDN, the request is redirected to the nearest server, ensuring that the content is delivered as quickly as possible.

The Advantages of Using a CDN
1. Improved Website Load Times: By caching content closer to the website visitors, CDNs reduce the amount of time it takes for the content to travel, thereby enhancing the user experience with faster page loads.
2. Reduced Bandwidth Costs: Through optimizations such as caching and other techniques, CDNs can significantly decrease the data an origin server needs to transfer, lowering hosting costs.
3. Increased Content Availability and Redundancy: CDNs can manage more traffic and withstand hardware failure better than a single origin server, ensuring that the website remains operational even under heavy loads or during hardware failures.
4. Enhanced Security Measures: Modern CDNs come equipped with robust security features like DDoS protection, Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), and SSL/TLS encryption, ensuring that both the content and the users are safeguarded from various cyber threats.
CDN vs. Web Hosting
It's crucial to distinguish between CDN services and web hosting since they serve different purposes. Web hosting involves storing the actual content of a website, including all its files, on a single server. In contrast, a CDN does not host content in the traditional sense but caches content across a network of servers to speed up access to data stored by the web host.
Popular CDN Providers
Notable CDN providers include Akamai Technologies, Amazon CloudFront, Cloudflare, and others, each offering a variety of services tailored to improve website performance and security across the globe.
Choosing a CDN: Key Considerations
When selecting a CDN provider, consider factors such as geographical coverage, performance, security features, scalability, traffic management capabilities, and cost. It's essential to choose a provider that aligns with your specific needs, whether you're targeting a global audience or focusing on specific regions.
The Impact on SEO
CDNs can significantly impact SEO by improving website loading times, a critical factor in user experience and, by extension, search engine rankings. Faster websites not only retain visitors but also contribute to higher engagement rates and conversion, which are positively regarded by search engines like Google.
---
As digital content consumption continues to rise, the importance of CDNs in the online ecosystem cannot be overstated. By enhancing speed, security, and availability, CDNs not only improve the user experience but also support website owners in managing bandwidth costs and boosting their site's SEO performance. As we move further into 2024, the role of CDNs in shaping the digital landscape remains pivotal, making them an indispensable asset for websites aiming to serve a global audience efficiently and securely.